Vol.26 Tailored Hair by Aki – Haircut, Perm: Hair Science Theory Edition
11.14.2023
Today I hope to simplify an otherwise complex process.
How does a perm occur? It is quite fascinating. To take straight hair and reconfigure it to bend and keep its new form.
The process of bending hair can be largely broken down into 3 parts.
1、Hydrogen bond
2、Cystine bond
3、Protein thermal reformation
A bit complicated, I know.
I will break down parts 1 and 2 into more simple terms.
1、Hydrogen bonds are bonds that are broken by water and are set when the hair dries.
Wet (broken) → Dry (joined)
2、A cystine bond is a bond that is broken down by the perming solution.
It is set depending on the reduction and oxidation caused by the perming solution.
Reduction (broken)→ Oxidation (joined)
3、Protein thermal reformation is a method in which we utilize the properties of protein that harden with heat.
Heat→Set
I will go into more detail on this in the next article.
1)The first is usually the process of taking a hair dryer and round brush to curl the hair, using a curling iron, or straightening the hair with a flat iron. Basically, with a hydrogen bond, the hair will return to its original state once it is wet.
2)On the other hand, with the perm process the hair will not regress to its original even if it is wet.
However, 1 and 2 share the same principles, as pictured below.
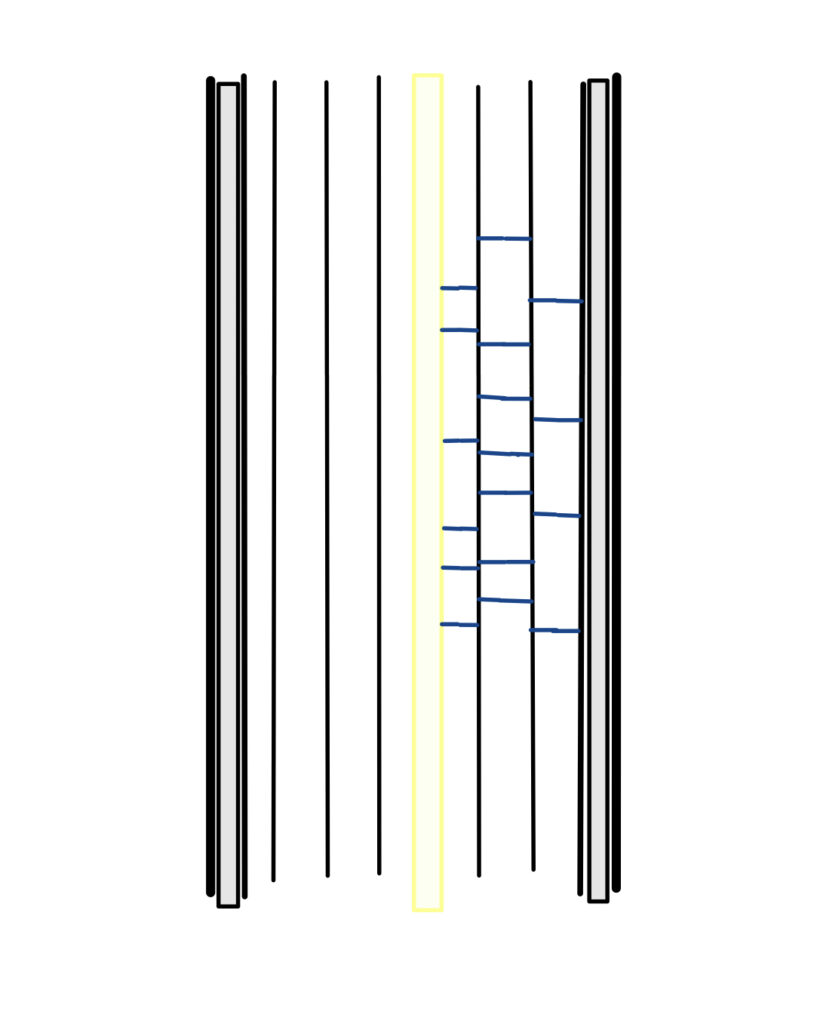
The hair contains many vertical fibers that are packed within it.
The bonds that connect horizontally are the hydrogen bonds, as well as the cystine bonds.
These bonds are temporarily broken with either water or a perming solution.
Reducing agents for breaking these bonds include thioglycolic acid, cysteamine, sulfite, GMT, and Spiera, among others. Each is selected and used according to the strength and textural characteristics of the hair and its condition, while also controlling the pH balance.
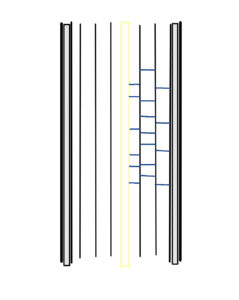
We then take these broken bonds and wrap the hair around rollers or perming rods, essentially bonding them in this misaligned state.
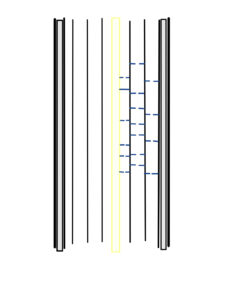
In the case of hydrogen bonds, the bond is set as the water evaporates and disappears.
In the case of perms, the bond is set by oxidizing them with an oxidizing agent such as bromic acid, or hydrogen peroxide.
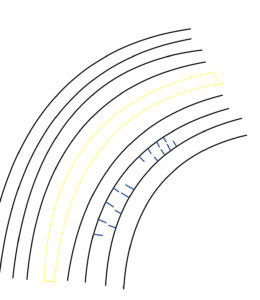
These are the processes of how a curl is set when using hot curlers or a curling iron, and how the curl is set when permed.
I think it is interesting to be able to picture them in simple terms.
As a supplement, heat is used to bond hydrogen bonds with curlers and irons. The bonds are set as the heat cools. If you make sure to allow enough time for your hair to cool down when styling, the process will be much smoother and last longer.
When styling your perm, the shape is maintained by both the heat and hydrogen bonds, so be conscious of how you dry your hair.
Our next discussion will be on setting a curl through protein thermal reformation.