Vol.38 Tailored Hair by Aki : Color Edition-Mechanism of Hair Coloring
05.15.2024
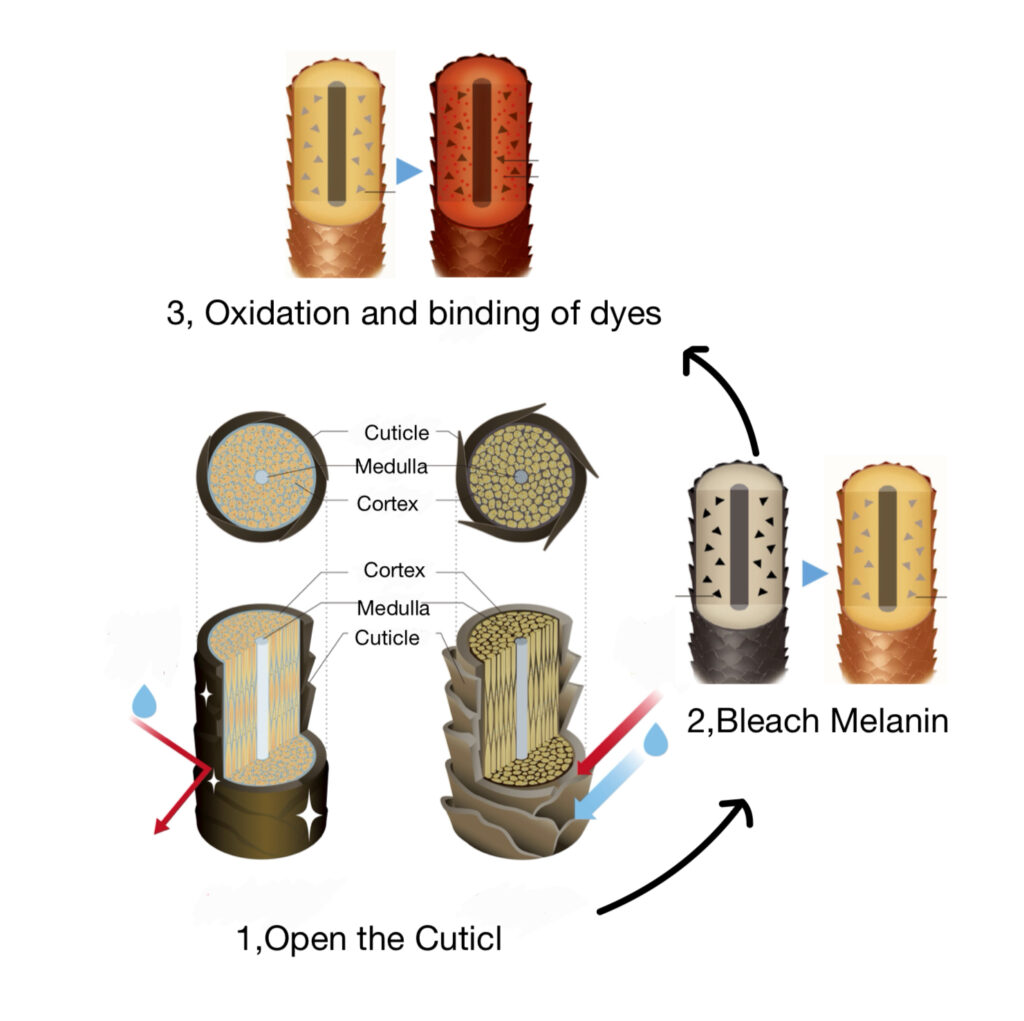
Today, let’s delve into why hair is dyed by hair colorants and explore the mechanism behind it. The process by which hair is dyed by hair colorants is based on chemical reactions, primarily consisting of four steps.
1. Function of Alkaline Agent: Hair color formulas contain alkaline agents, which play a role in opening the hair’s cuticle layer. By opening the cuticle, the dye can penetrate the hair’s internal structure (cortex) more easily.
2. Changes in the Pigment of Hair Melanin: The natural color of hair is determined by melanin pigment. Alkaline agents and hydrogen peroxide (bleaching agent) from the hair colorant penetrate the hair’s interior and bleach or breakdown the natural pigment. This lightens the original color, making it easier to apply a new color.
3. Oxidation and Binding of Dye: Precursors of the dye in the hair colorant react with hydrogen peroxide to become oxidized, activating them as pigments. These activated pigments bond to the hair’s interior, forming a new color.
4. Bound Color: Lastly, the components of the hair colorant react within the hair cortex, binding the pigments and holding the color. This reaction results in the hair being dyed a new color, which is resistant to washing out.
Dying hair with colorants is achieved through these multiple chemical processes. The type of coloring (semi-permanent, demi-permanent, permanent, etc.) determines the degree of impact on the hair and longevity of the color. Semi-permanent colors are relatively gentle on the hair, providing temporary color, while permanent colors penetrate deeper, offering long-lasting color.
Ammonia is commonly used in many alkaline agents. It is often disliked for its distinct odor, but one of its characteristics is its high volatility. The purpose is to use substances that easily vaporize and do not remain in the hair.